Receiving UDP/RTP
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is the most popular protocol for delivering digital TV in local networks, including those in hospitality organizations and internet provider city networks. As a connectionless protocol, UDP does not provide any error-checking or correction mechanisms. This makes it a faster and more lightweight protocol than TCP.
Media Address Format
UDP address is used to identify the location of the media stream that is being transmitted over the network
udp://address
udp://address:port
udp://interface@address:port#options
interface- name of the network interface, such aseth0, to receive UDP stream. If not defined, the UDP stream will be received according to the system routesaddress- IPv4 address of the UDP stream, It could be a multicast group or a local interface IP address to receive unicast streamsport- network port to receive the UDP stream. If not specified, the default value is1234
Additional Options:
src=IP- UDP multicast source address for IGMPv3. Should be enabled IGMPv3 in linux settings: Configure IGMP Version. Available from version 230303 and latersync- receives UDP in separate thread with bitrate syncingno_sync- disables bitrate syncing if enabled globallyrenew=seconds- interval for renewing the multicast subscription. Usually operation renew IGMP subscription automaticallysocket_size=bytes- size of the system socket, with the default value taken from:sysctl net.core.rmem_default
Examples of UDP addresses:
udp://127.0.0.1:10001- receives the stream on localhost using port 10001. This can be useful for transferring streams between different services, like receiving a transcoded stream from FFmpegudp://eth0@239.255.1.1#pnr=100- receives multicast group 239.255.1.1 on the eth0 interface. The optionpnrenables stream demultiplexing and selects program number 100
Web Interface
To configure a new UDP input using the Web Interface, begin by selecting "New Stream" from the main menu. Then, in the Input List, click on the gear icon and set the "Input Type" to UDP. Alternatively, you can modify an existing stream by opening its settings, adding a New Input, and clicking on the corresponding gear icon.
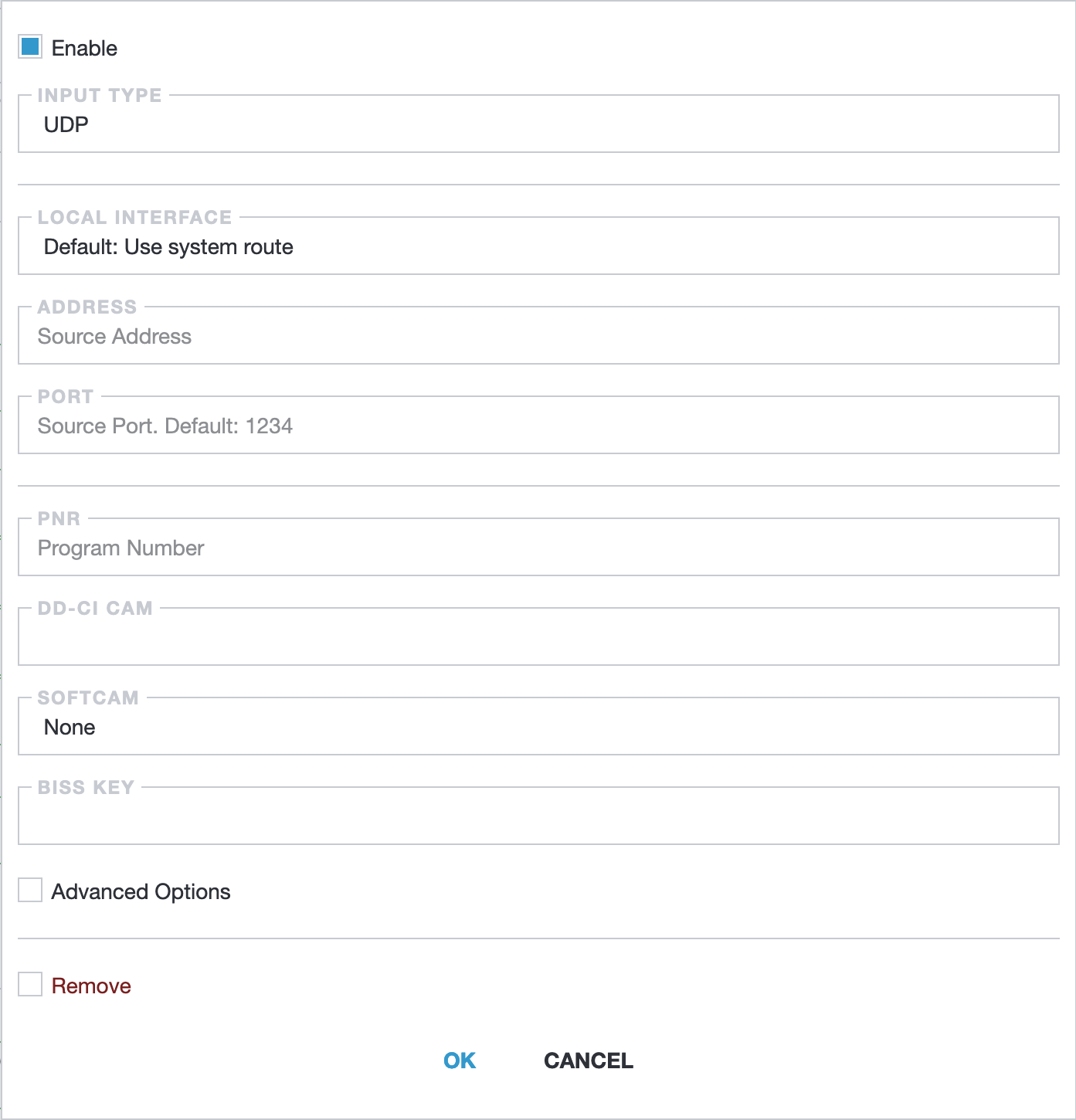
Most options presented in the web interface correspond directly to the components of the UDP address, as described in the "Media Address Format" section. However, there are also some additional options you might find useful:
PNR- program number for MPTS streams. When defined, it enables stream demultiplexing and selects the program with the specified numberDD-CI CAM- this option is now deprecated and has been replaced by virtual adapters. More information can be found in ...Softcam- selects a descrambler for the CAM Client. You can learn more about this in ...BISS Key- key for the BISS CAS descrambler. More details can be found in Decrypt streams with BISS CAS
There are also advanced options available for further customization:

Please use the advanced options only if you understand their implications
Troubleshooting
Find more information in Troubleshooting UDP reception